When it comes to choosing the best Large Language Model (LLM) for coding, the clear answer depends on your specific needs, but Claude 3.5 Sonnet is currently widely regarded as the top-performing model for complex logic, debugging, and architectural reasoning. For developers seeking the best all-around integration and speed, GPT-4o remains a powerful contender. If you are looking for the best open-source performance, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 and Codestral offer state-of-the-art capabilities that rival proprietary models.
Introduction: The Era of AI-Augmented Software Engineering
The landscape of software development has been fundamentally altered by the rise of Large Language Models. No longer just simple autocomplete tools, modern LLMs act as “AI pair programmers” capable of writing entire modules, refactoring legacy code, and identifying security vulnerabilities in seconds. However, with new models being released almost monthly, choosing the right one for your workflow is critical for maximizing productivity and code quality.
This article explores the top coding models based on industry benchmarks, real-world performance, and the specific strengths of each platform. Whether you are building a React frontend, a Python backend, or complex C++ systems, understanding the nuances of these models will help you ship better code faster.
1. Claude 3.5 Sonnet: The Current Gold Standard
Claude 3.5 Sonnet, developed by Anthropic, has quickly become the favorite among professional software engineers. Its rise to the top is driven by its exceptional “reasoning” capabilities, which allow it to understand complex project structures rather than just individual lines of code.
-
Logical Reasoning: Claude 3.5 Sonnet excels at following multi-step instructions and maintaining logic across large files. This makes it particularly effective for refactoring tasks where the AI must understand how a change in one function affects the rest of the system.
-
Artifacts UI: Anthropic’s “Artifacts” feature allows developers to see code execution or UI renders in a side-by-side window, creating a seamless feedback loop for frontend development.
-
Superior Benchmarks: On the HumanEval benchmark (a standard test for coding proficiency), Claude 3.5 Sonnet consistently outscores its competitors, particularly in Python and JavaScript.
-
Reduced Hallucinations: Compared to earlier models, Claude 3.5 Sonnet is less likely to “hallucinate” or invent non-existent library functions, leading to more reliable and runnable code.
2. GPT-4o: The Versatile All-Rounder
OpenAI’s GPT-4o (the “o” stands for Omni) is the backbone of many popular coding tools, including GitHub Copilot. While Claude may lead in pure logic, GPT-4o is arguably the most versatile and accessible model on the market today.
-
Speed and Efficiency: GPT-4o is significantly faster than its predecessor, GPT-4 Turbo. This low latency is essential for real-time code completion where even a one-second delay can break a developer's flow.
-
Multimodal Capabilities: GPT-4o can process images and text simultaneously. This is incredibly useful for developers who want to upload a screenshot of a UI design and ask the AI to generate the corresponding CSS and HTML code.
-
Deep Integration: Because OpenAI powers GitHub Copilot and is integrated into Microsoft’s ecosystem, GPT-4o benefits from being “where the code lives,” providing context-aware suggestions based on your entire repository.
-
Broad Language Support: While all LLMs handle Python well, GPT-4o shows remarkable stability across a massive range of languages, including niche or older languages like COBOL or Fortran.
3. DeepSeek-Coder-V2: The Open-Source Powerhouse
DeepSeek has disrupted the AI industry by releasing models that perform at the level of GPT-4 while remaining open-weights. DeepSeek-Coder-V2 is a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that has set new records for open-source coding performance.
-
Massive Language Support: DeepSeek-Coder-V2 supports over 300 programming languages, making it the most linguistically diverse coding model available.
-
Unbeatable Value: For teams looking to self-host or use an affordable API, DeepSeek offers a performance-to-price ratio that proprietary models cannot match.
-
State-of-the-Art Benchmarks: It is the first open-source model to surpass GPT-4 Turbo on several coding-specific benchmarks, particularly in complex math and logic-based programming.
-
Mixture-of-Experts Architecture: By only activating a fraction of its parameters for each query, DeepSeek-Coder-V2 maintains high intelligence while keeping inference costs and energy consumption low.
4. Codestral by Mistral AI: Built for Developers
Mistral AI, the French AI leader, released Codestral as its first dedicated model for code. It is designed specifically to be integrated into IDEs (Integrated Development Environments) and to help developers with “Fill-In-the-Middle” (FIM) tasks.
-
Optimized for FIM: Codestral is specifically trained to understand code that comes before and after a cursor, making it exceptionally good at completing logic within an existing function.
-
Large Context Window: With a 32k context window, Codestral can “read” significant portions of a project, ensuring that the code it generates is consistent with the established style and naming conventions of the repository.
-
Efficiency for Local Hosting: Despite its power, Codestral is optimized to run on relatively modest hardware compared to “frontier” models, making it a candidate for local development environments where data privacy is paramount.
5. Llama 3 (70B): Meta’s Generalist for Code
While Meta’s Llama 3 is a general-purpose model, its 70B parameter version has proven to be an excellent coder. It serves as the base for many fine-tuned coding models found on platforms like Hugging Face.
-
Excellent Instruction Following: Llama 3 is highly responsive to “System Prompts,” allowing developers to strictly define the coding style, documentation requirements, and libraries the AI should use.
-
Broad Community Support: Because Llama 3 is open-weights, the developer community has created “Llama-3-70B-Instruct” versions specifically optimized for Python, Java, and other major stacks.
-
High Availability: Llama 3 is available on almost every major cloud provider (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), making it easy to deploy within existing enterprise infrastructure.
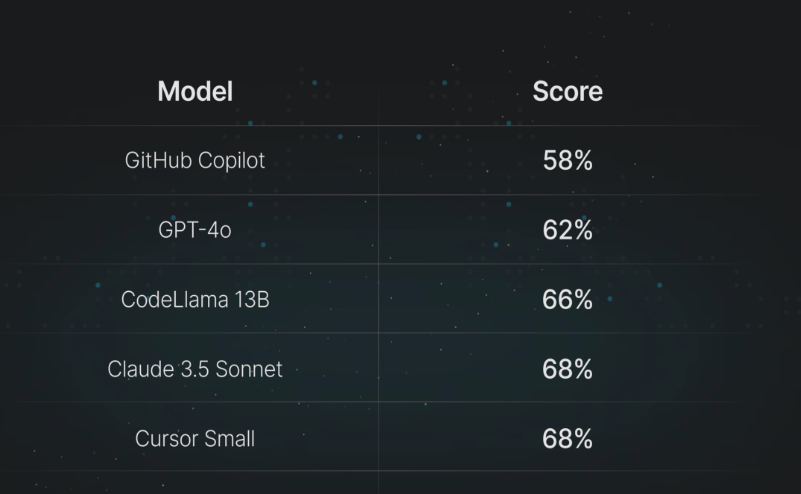
Key Benchmarks: How the Models Compare
To choose the best LLM, it is helpful to look at standardized metrics. The most common metrics are HumanEval (solving Python problems) and MBPP (Mostly Basic Python Problems).
-
Claude 3.5 Sonnet: HumanEval score of ~92%. Best-in-class for zero-shot coding.
-
GPT-4o: HumanEval score of ~90%. Extremely consistent across multiple trials.
-
DeepSeek-Coder-V2: HumanEval score of ~90%. Highest among open-weights models.
-
Codestral: HumanEval score of ~81%. Strongest in the mid-size parameter category.
Note: Benchmark scores can vary based on testing methodology, but the ranking generally places Claude 3.5 and GPT-4o at the top.
Choosing the Right Tool: The Role of the IDE
An LLM is only as good as the interface through which you use it. For coding, the model provides the “brain,” but the tool provides the “context.”
-
Cursor: This is currently the most popular AI-powered IDE. It allows users to toggle between Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4o. Cursor is unique because it indexes your entire codebase, allowing the LLM to “see” every file in your project.
-
GitHub Copilot: Powered primarily by OpenAI models, Copilot is the industry standard for “ghost text” (inline completions). It is best for developers who want a subtle, non-intrusive assistant.
-
Continue.dev: An open-source extension for VS Code and JetBrains that allows you to plug in any LLM via API. This is the best choice for developers who want to use DeepSeek or Codestral while maintaining privacy.
Why Claude 3.5 Sonnet Often Wins for Complex Tasks
Many developers report that while GPT-4o is excellent at generating “boilerplate” code (standard setup code), it often struggles with debugging complex logic compared to Claude 3.5 Sonnet. Claude’s architecture seems better suited for identifying the “root cause” of a bug.
When you provide a stack trace or an error log to Claude 3.5 Sonnet, it doesn't just suggest a fix; it explains why the error occurred and how the fix addresses the underlying architectural flaw. This educational component makes it a superior tool for senior developers who need a sounding board for complex systems design.
Considerations for Enterprise and Security
When selecting an LLM for a professional or corporate environment, performance is only one piece of the puzzle. Security and data privacy are equally important.
-
Data Privacy: Proprietary models like those from OpenAI and Anthropic offer “Enterprise” tiers that guarantee your code will not be used to train future versions of the model.
-
Local Execution: For companies with strict compliance requirements (such as finance or healthcare), using an open-source model like DeepSeek or Llama 3 hosted on internal servers ensures that no code ever leaves the company’s firewall.
-
Vulnerability Scanning: Some models are better than others at identifying security flaws (like SQL injection). GPT-4o has a slight edge here due to its extensive training on security-focused datasets.
How to Maximize the Output of a Coding LLM
Regardless of which model you choose, the quality of the code you get back is highly dependent on how you prompt the AI. To get the best results, follow these best practices:
-
Provide Context: Don't just ask for a function. Tell the AI which libraries you are using (e.g., “Use FastAPI and SQLAlchemy”).
-
Be Specific About Style: If your team uses a specific linting style or naming convention (e.g., “Use camelCase for variables”), include that in your prompt.
-
Iterative Prompting: If the AI makes a mistake, don't start a new chat. Correct it in the existing thread. LLMs are excellent at “learning” from their mistakes within a single session.
-
Ask for Tests: Always ask the LLM to “Write unit tests for the code above.” This not only gives you tests but often forces the AI to catch its own logic errors during the test-generation process.
Future Outlook: What’s Next for AI Coding?
The next frontier for coding LLMs is “Agentic Workflows.” We are moving away from a world where the AI simply suggests code, and toward a world where the AI can:
-
Identify a bug in a production log.
-
Locate the relevant file in the repository.
-
Write a fix.
-
Run the tests to verify the fix.
-
Open a Pull Request for a human to review.
Models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and future iterations of GPT-5 are being built with this agency in mind, focusing on long-term planning and tool-use capabilities.
Final Recommendations
To summarize the current state of coding LLMs:
-
Best for Complex Logic & Debugging: Claude 3.5 Sonnet. It is the most “intelligent” model for deep architectural work.
-
Best for Daily Workflow & Speed: GPT-4o. Its integration into tools like GitHub Copilot makes it the easiest to use.
-
Best for Open Source & Privacy: DeepSeek-Coder-V2. It offers world-class performance without the “black box” nature of proprietary software.
-
Best for Integration: Use Cursor as your IDE and swap between Claude and GPT depending on the task at hand.
By choosing the right model for the right task, developers can significantly reduce the “grunt work” of coding and focus on what truly matters: solving problems and building innovative software.