When you sleep, your normal heart rate usually drops to 40-60 beats per minute if you are an adult. Children and teens have higher sleeping heart rates, while athletes may see lower numbers. Tracking your heart rate during sleep helps you spot changes that might signal health issues. Your genetics, age, fitness, and even stress can affect your sleeping heart rate. If your sleeping heart rate falls below 40 or rises above 100 beats per minute, or you notice symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath, you should talk to a doctor. Good sleep health supports your body and mind every day.
Key Takeaways
Your heart rate often slows to 40-60 beats per minute when you sleep if you are an adult. Children and athletes can have different normal heart rates. Tracking your heart rate while you sleep can help you notice health changes early. It also helps you sleep better and keeps your heart healthy. Stress, age, fitness, medicines, and how well you sleep can change your heart rate at night. Wearable devices like smart rings can help you check your heart rate while you sleep. They also help you learn about your sleep patterns. If your heart rate is less than 40 or more than 100 beats per minute while you sleep, or if you feel chest pain or dizzy, you should see a doctor right away.
Resting vs. Sleep Heart Rate

Key Differences
You might wonder how your resting heart rate compares to your heart rate during sleep. Both numbers help you understand your body’s health, but they are not the same. Your resting heart rate measures how many times your heart beats per minute when you are awake, calm, and not moving. Most adults have a resting heart rate between 60 and 100 beats per minute. When you are sleeping, your heart rate drops lower than your resting heart rate. This happens because your body relaxes and uses less energy.
Here is a simple table to show the difference:
State | Typical Heart Rate (bpm) |
|---|---|
Resting | 60-100 |
Sleeping | 40-60 |
Your normal heart rate during sleep is usually slower than your resting heart rate. Children and teens have higher sleeping heart rates, while athletes may see lower numbers. You can use these numbers to check if your heart is working well.
Tip: If you notice your sleeping heart rate is much higher or lower than your normal heart rate, you should talk to a doctor.
Health Insights
Tracking your resting heart rate and your heart rate during sleep gives you clues about your health. A lower resting heart rate often means your heart is strong. When you sleep, your heart rate drops even more. This helps your body recover and repair itself. If your normal heart rate does not slow down during sleep, it could mean you have stress or a health problem.
You can use smart devices to watch your sleeping heart rate. These tools help you see patterns and changes over time. Good sleep and heart health go together. If you keep your resting heart rate and sleeping heart rate in the normal range, you support your body’s health. You should pay attention to changes in your sleep and heart rate. This helps you catch problems early and stay healthy.
Normal Sleeping Heart Rate Ranges
Adults
When you sleep, your heart rate gets lower than when you are awake. Most adults have a sleeping heart rate between 40 and 60 beats per minute. This helps your body rest and fix itself at night. If you are healthy, your heart rate during sleep stays in this range. A normal sleeping heart rate means your heart is working well.
Sometimes, your heart rate while sleeping can go below 40 or above 100 beats per minute. This can happen because of health problems or medicine. Some causes are heart disease, sleep apnea, or issues with your heart’s electrical system. You might feel dizzy, tired, or have trouble breathing if your heart rate is too low. If your heart rate goes over 100 beats per minute, you might have tachycardia. You should see your doctor if you notice these changes or feel sick.
Note: If your sleeping heart rate is under 40 or over 100, it could mean something is wrong. Always talk to your doctor if you feel bad.
Common causes of abnormal sleeping heart rate in adults:
Coronary artery disease
Valve disease
Sleep apnea
Medication effects (such as beta-blockers)
Electrolyte imbalances
Heart muscle damage
Symptoms to watch for:
Chest pain
Dizziness or fainting
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Confusion
Children & Teens
Kids and teens have faster sleeping heart rates than adults. Their hearts beat quicker because they are still growing. For children, a normal sleeping heart rate is between 70 and 110 beats per minute. As kids get older, their sleeping heart rate slowly goes down.
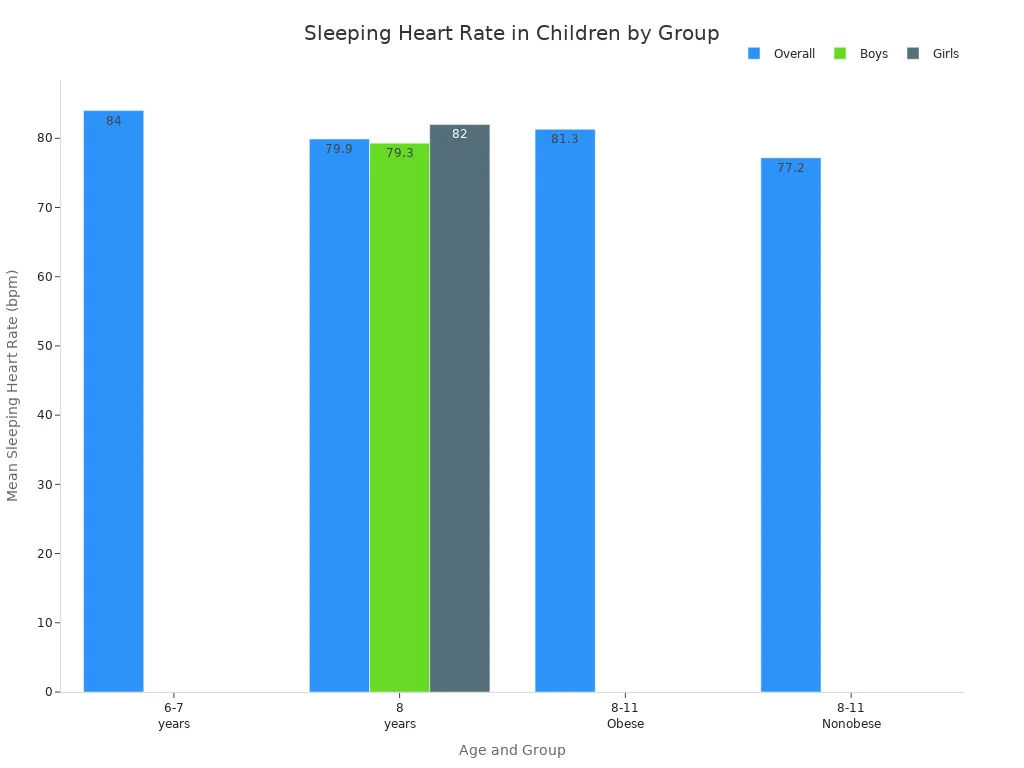
Here is a table that shows average sleeping heart rates for kids by age group:
Age (years) | Group | Mean Sleeping Heart Rate (bpm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
6-7 | Overall | ~83 – 85 | Younger children have faster rates |
8 | Overall | ~80 | Average for Cleveland cohort |
8 | Boys | ~78 – 80 | Boys have slower rates than girls |
8 | Girls | ~82 | Girls have faster rates than boys |
8-11 | Obese children | ~79 – 83 | Obese children have faster rates |
8-11 | Nonobese children | ~75 – 79 | Nonobese children have slower rates |
8-11 | African American | Faster than Caucasians | African American children have faster rates than Caucasians |
Teens have a lower sleeping heart rate as they get older. Over five years, the average sleeping heart rate for teens drops by about 11 beats per minute. Girls usually have a faster sleeping heart rate than boys. How fit you are can also change these numbers. During REM sleep, heart rates are higher than during NREM sleep.
Common causes of abnormal sleep heart rate in children and teens:
Cause/Condition | Description and Characteristics |
|---|---|
Premature contractions | Extra beats; often no cause found; usually no treatment needed; common in normal children and teens. |
Sinus tachycardia | Fast heart rate; can be normal or caused by fever, stress, or thyroid activity. |
Supraventricular tachycardia | Rapid heart rate due to abnormal signals; symptoms include palpitations, dizziness, fainting. |
Long QT Syndrome | Disorder of heart's electrical system; may cause fainting, seizures, sudden death; needs medical management. |
Bradycardia | Slower-than-normal heart rate; can be normal in athletic teens; may be caused by heart block or sick sinus syndrome. |
Sick sinus syndrome | Sinus node dysfunction; symptoms include fatigue, dizziness; often related to congenital heart disease. |
Complete heart block | Signals blocked between atria and ventricles; causes slow heart rate; may require pacemaker. |
Seniors
As you get older, your sleeping heart rate can change. Seniors usually have a sleeping heart rate between 50 and 70 beats per minute. This is a little higher than younger adults. Getting older can make it harder for your heart to slow down at night. Some seniors have a healthy sleeping heart rate close to 70 beats per minute.
Your sleeping heart rate may change if you take medicine or have heart problems. Heart muscle damage, metabolism issues, or sleep apnea can also affect your heart rate. If your sleeping heart rate is below 40 or above 100, you should talk to your doctor.
Athletes
If you play sports a lot, your sleeping heart rate may be lower than most people’s. Exercise makes your heart stronger and helps it pump blood better. Many athletes have a sleeping heart rate below 50 beats per minute. This shows their hearts are strong and healthy.
A normal sleeping heart rate for athletes is between 35 and 50 beats per minute. Your heart rate can drop even lower during deep sleep. This is normal for people who train often. If you feel dizzy, tired, or have chest pain, you should see your doctor.
Tip: Watching your sleep heart rate helps you know how well your body recovers and how fit you are.
Summary Table: Normal Sleeping Heart Rate Ranges
Group | Typical Sleeping Heart Rate (bpm) |
|---|---|
Adults | 40-60 |
Children | 70-110 |
Teens | 60-100 |
Seniors | 50-70 |
Athletes | 35-50 |
A normal sleeping heart rate is good for your health and helps your body heal while you sleep. You should check your sleeping heart rate to find changes early. A healthy sleeping heart rate means your heart works well at night. If your sleeping heart rate is not in the normal range or you feel sick, you should talk to your doctor.
Factors Affecting Heart Rate During Sleep
Age & Fitness
Your age and fitness level play a big role in what can affect sleeping heart rates. As you grow from a child to an adult, your sleeping heart rate usually drops. Young children can have a sleeping heart rate that is about 20 beats per minute higher than older kids. When you get older, your heart changes shape and size, which helps lower your sleeping heart rate. If you stay active and fit, your heart becomes stronger. People who exercise often have a lower sleeping heart rate. More body fat, measured by skinfold thickness, can raise your sleeping heart rate. Good physical activity helps improve sleep quality and keeps your heart healthy.
Children: Sleeping heart rate drops as you age.
Fitness: More activity means a lower sleeping heart rate.
Body fat: Higher fat can increase sleeping heart rate.
Stress & Lifestyle
Stress can change your sleeping heart rate. When you feel stressed, your body releases hormones that make your heart beat faster. This can keep your heart rate high even when you try to sleep. Chronic stress may cause your heart rate to stay up for a long time, which can hurt your sleep quality. If you have a lack of sleep, your body cannot recover well, and your sleeping heart rate may rise. Lifestyle choices like smoking or drinking alcohol also affect your heart and sleep. These habits can make it harder for your body to relax at night.
Tip: Try to manage stress and avoid unhealthy habits to help your sleeping heart rate stay in a healthy range.
Medications & Health Conditions
Some medicines and health problems are part of what can affect sleeping heart rates. Medications for blood pressure, asthma, or mental health can change how your heart beats at night. Health conditions like sleep apnea, heart disease, or diabetes can also raise or lower your sleeping heart rate. If you have a lack of sleep because of these issues, your heart may work harder during the night. Always talk to your doctor if you notice big changes in your sleeping heart rate or if you feel unwell.
Sleep Stages
Your heart rate changes as you move through different sleep stages. During deep sleep, also called slow wave sleep, your heart rate drops to its lowest point. This stage helps your body recover and repair. In REM sleep, your heart rate goes up and becomes more variable. The table below shows how heart rate changes in each sleep stage:
Sleep Stage | Heart Rate | Body Response |
|---|---|---|
Slow Wave Sleep (Deep) | Lower | More rest, high quality recovery |
Higher | More active, dreams, less recovery |
If you have a lack of sleep or poor sleep quality, you may spend less time in deep sleep. This can keep your sleeping heart rate higher than normal. Good sleep habits help you get enough deep sleep and keep your heart healthy.
Monitoring Sleep Heart Rate

Wearables & Devices
You can now track your sleep heart rate easily with smart wearables. Devices like the VERTU Aura Ring help you see how your heart works while you sleep. The Aura Ring looks like a piece of fine jewelry, but it works as a powerful health tool. It uses advanced AI to monitor your sleep patterns, heart rate, blood oxygen, blood pressure, and even glucose levels. You get all this information without any needles or discomfort.
The Aura Ring fits comfortably on your finger. It feels light and moves with your hand, so you can wear it all night. The ring connects to an app on your phone, where you can check your sleep data and get weekly wellness reports. You also get expert support if you have questions about your health. The battery lasts up to 10 days, so you do not have to worry about charging it every night.
Tip: A wearable like the Aura Ring helps you understand your sleeping heart rate and spot changes early. This can help you improve your sleep quality and overall health.
Tracking Tips
To get the most out of your sleep heart rate tracking, you should follow some best practices:
Choose a wearable that matches your needs for sleep and heart rate monitoring.
Look for devices that are easy to use and have clear instructions.
Make sure your device fits well and stays in contact with your skin during sleep.
Use the app to check your sleep patterns and heart rate trends over time.
Ask for help from health experts if you have trouble using your device or understanding your data.
Stay engaged by checking your progress and celebrating improvements in your sleep quality.
Pick a device that is made for tracking sleeping heart rate.
Use the same device each night to keep your data consistent.
Work with your doctor if you want to add your sleep data to your health records.
Look for devices that have medical certifications for extra trust.
Remember that wearables help you learn about your sleep, but they do not replace medical advice.
You can use wearables like the Aura Ring to track your sleeping heart rate with ease. These tools give you clear feedback and help you make better choices for your sleep and health.
When Sleep Heart Rate Is Abnormal
Warning Signs
You may not always notice when your sleeping heart rate is abnormal. Your body gives you warning signs that you should not ignore. If you wake up feeling tired even after a full night of sleep, your heart may not be slowing down as it should. You might feel your heart racing or skipping beats during the night. Sometimes, you may wake up short of breath or with chest pain. These symptoms can point to a high sleeping heart rate or a low sleeping heart rate.
Look for these warning signs:
Chest pain or tightness while resting or sleeping
Irregular heartbeat or fluttering in your chest
Shortness of breath, even when lying down
Dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting spells
Swelling in your legs or abdomen
Waking up gasping for air or choking
If you notice any of these signs, your sleeping heart rate may be outside the normal range. This can be a sign of a serious problem with your heart or your sleep.
Ignoring these warning signs can lead to bigger health problems. Studies show that abnormal sleeping heart rate, especially when linked to sleep deprivation, raises your risk for heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and even sudden cardiac death. Your heart needs to slow down during sleep to recover. If it does not, your body stays in a state of stress. This can damage your heart’s electrical system and blood vessels. Over time, you may develop inflammation, insulin resistance, or gain weight, which makes sleep and heart health worse.
When to Seek Help
You should know when a heart rate is dangerous. If your sleeping heart rate drops below 40 beats per minute or rises above 100 beats per minute, you need to pay attention. These numbers can mean your heart is under stress or not working right. You should also ask yourself, “When is a heart rate dangerous for me?” If you have symptoms like chest pain, fainting, or trouble breathing, you should get medical help right away.
Doctors say you should seek help if you notice:
Chest pain that does not go away
Irregular or very fast heartbeats during sleep
Shortness of breath that wakes you up
Swelling in your legs or belly
Feeling tired all the time, even after good sleep
Symptom | What It Might Mean | What To Do |
|---|---|---|
Chest pain | Heart strain or blocked arteries | Call your doctor right away |
Irregular heartbeat | Arrhythmia or heart rhythm problem | Get checked soon |
Shortness of breath | Heart or lung issue | Seek help quickly |
Swelling in legs/belly | Heart not pumping well | See a doctor |
Constant fatigue | Heart not resting during sleep | Ask for a check-up |
Treating sleep disorders early can protect your heart. If you have sleep apnea or another sleep problem, your doctor can help you find the right treatment. Treating sleep disorders helps your heart slow down at night and lowers your risk for serious problems. You should aim for 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep each night. This gives your heart and blood vessels time to recover.
Remember, your sleeping heart rate is a key sign of your health. If you notice changes or feel unwell, do not wait. Getting help early can prevent heart failure, stroke, or sudden cardiac death.
Ignoring abnormal sleeping heart rate can lead to dangerous health issues. You can protect yourself by watching for warning signs, treating sleep disorders, and knowing when a heart rate is dangerous. Your heart works hard every night. Give it the care it needs.
You can protect your heart by knowing your healthy sleeping heart rate. Tracking your sleep helps you spot changes early. You support your body by following simple habits for better sleep:
Move your body during the day, but rest before sleep.
Limit artificial light before sleep and use blue light filters.
Avoid eating or drinking close to sleep time.
Make your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet for better sleep.
If you notice changes in your sleep heart rate or feel unwell, use health devices and talk to your doctor. Everyone’s sleep is different. Watching your sleep helps you stay healthy.
FAQ
What is the best way to measure my heart rate while sleeping?
You can use a wearable device like the VERTU Aura Ring. It tracks your heart rate automatically while you sleep. The ring sends data to your phone, so you see your results each morning.
Can stress make my sleeping heart rate higher?
Yes, stress can raise your sleeping heart rate. Your body releases hormones that make your heart beat faster. Try deep breathing or relaxing activities before bed to help lower your heart rate.
Tip: Calm your mind before sleep for a healthier heart rate.
Is it normal for my heart rate to change during sleep?
Your heart rate changes as you move through sleep stages. It drops during deep sleep and rises during REM sleep. These changes help your body recover and rest.
Sleep Stage | Heart Rate Change |
|---|---|
Deep Sleep | Lower |
REM Sleep | Higher |
Should I worry if my sleeping heart rate is below 40 bpm?
If your sleeping heart rate drops below 40 bpm and you feel dizzy, weak, or short of breath, you should talk to your doctor. Some athletes have low heart rates, but symptoms mean you need a check-up.
Note: Always listen to your body and seek help if you feel unwell.