Innovative smartphone security is changing how people keep their data safe in 2025. Fancy devices like the Vertu Quantum Flip set higher standards in mobile technology with strong encryption and smart AI features. Recent numbers show cybercrime costs might reach $10.5 trillion around the world, and almost half of all breaches use personal information. Mobile technology now has new dangers, so users need better security. The Vertu Quantum Flip is leading, making new rules for privacy and safety in mobile technology.
Key Takeaways
-
New smartphone security uses passwordless logins, AI, and quantum encryption to keep data safe and stop attacks.
-
AI-powered attacks and deepfake scams are growing, so users need to watch out and learn how to spot threats.
-
Multi-factor and device-based authentication make logging in safer and help block many cyberattacks.
-
Updating your phone and checking app permissions help stop security risks and keep your data from leaking.
-
Learning good security habits and using strong protections keep your phone and personal data safe now and later.
Trends
Innovative Smartphone Security
Smartphones in 2025 use new security to keep users safe. Many phones now let you log in without a password. This helps stop phishing, which got much worse in late 2024. People like passwordless logins because they are easy. Most users, about 70%, say they want things to be simple. Banks now use device-based authentication instead of SMS codes. This makes logging in safer by using a special Mobile ID key for each person.
Luxury phones like the Vertu Quantum Flip have better protection. These phones use quantum encryption and AI-powered security to guard your data. Owners get real-time threat alerts and privacy-first logins. Strong privacy laws make companies check age and identity without sharing private info. CISOs now work to stop attacks before they happen. About 87% say protecting information is their main goal.
Note: Most people want security that is fast and easy. Seamless authentication is now the top choice.
Here are some big trends in smartphone security:
-
Passwordless logins help stop phishing.
-
AI-powered features find threats fast.
-
Device-based logins are safer than SMS codes.
-
Privacy-first systems keep user data safe and follow new laws.
-
Proactive defense stops attacks early.
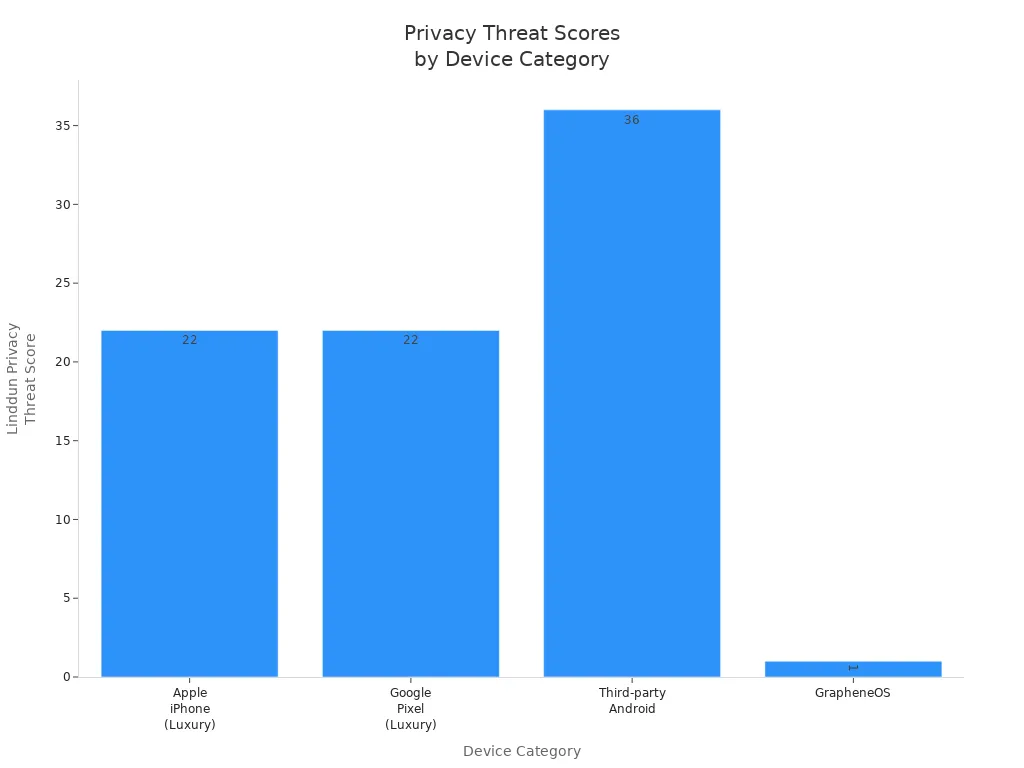
The table below shows how luxury phones compare to regular ones:
|
Device Category |
Key Security Features and Strengths |
Key Privacy Weaknesses and Risks |
Linddun Privacy Threat Score (Lower is Better) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Apple iPhone (Luxury) |
On-device data processing, app privacy labels, end-to-end encryption (iMessage, FaceTime, iCloud) |
Mandatory Apple ID, behavioral tracking, limited transparency, data sharing |
22 |
|
Google Pixel (Luxury) |
Federated learning, frequent security updates, customizable privacy settings |
Data sharing with third parties, default tracking enabled, advertising model conflicts |
22 |
|
Third-party Android |
Affordability, wide feature range |
Pre-installed bloatware, data monetization, inconsistent security updates |
36 |
|
GrapheneOS (Privacy-focused AOSP fork) |
Application sandboxing, isolated profiles, MAC address randomization, no mandatory accounts |
Limited app compatibility, requires technical expertise |
1 |
AI and Quantum Encryption
AI and quantum encryption are important for phone security. Phones like the Vertu Quantum Flip use quantum encryption to protect messages and files. This makes it very hard for hackers to break in. AI-powered security adds more protection. Phones use AI to look for threats and block them right away.
AI-powered facial recognition lets users unlock phones safely. The phone checks your face to make sure it is you. On-device AI keeps your data private because the phone does the work itself. This makes phones safer and faster.
Advanced protection uses both AI and quantum encryption for strong security. These systems keep your data safe and private. Ethical AI helps protect sensitive data. Companies make these features to follow strict privacy rules and stop new attacks.
Tip: AI-powered security can find strange actions and stop fraud early.
Phones in 2025 use these new protections to stay ahead of hackers. Luxury phones lead by giving the best security and privacy.
Threats

AI-Powered Attacks
Cybercrime is getting worse in 2025. Attackers use artificial intelligence to make new attacks on smartphones. AI-powered attacks send fake messages and calls that seem real. Attackers copy how people write and talk. They use AI to run phishing scams and make fake voices. These tricks make it hard for people to spot scams. It is harder to stop data breaches now.
Some common AI-powered attack methods are:
-
Pop-up phishing and watering hole phishing trick users to share info.
-
Voice phishing, or vishing, uses fake voices to pretend to be trusted people.
-
Ransomware comes through phishing messages.
-
Phishing-as-a-service lets less skilled attackers use advanced tools.
-
AI-powered malware changes itself to avoid being found and spreads alone.
Experts think AI-powered attacks will go up by 45% this year. These attacks often cause data breaches. They show weak spots in mobile devices. Mobile malware now uses AI to find important files and systems. This makes it harder to defend against attacks.
Deepfake Scams
Deepfake scams are now a big problem for mobile users. Attackers use AI to make fake videos and voices that look and sound real. Many people cannot tell what is real or fake. This causes more data breaches and money loss.
|
Aspect |
Statistic / Insight |
|---|---|
|
Daily exposure to mobile scams |
44% of mobile users face scams daily globally; 51% in the US, 49% in the UK, 38% in DACH region |
|
Difficulty identifying scams |
66% struggle to distinguish scams from legitimate content; only 15% confident in spotting scams |
|
Financial impact |
52% of victims report monetary loss or fraud |
|
Emotional impact |
75% of victims suffer severe emotional consequences; 46% report long-term mental health effects (anxiety, depression, loss of trust) |
|
Vulnerability of younger users |
58% of Gen Z encountered deepfake/sextortion scams; 28% fell victim (double Gen X rate, four times Boomers) |
|
Underreporting |
Only 17% of victims report scams; 14% for younger users |
|
Industry response |
Launch of Scam Guard by Malwarebytes for real-time scam detection and user education |
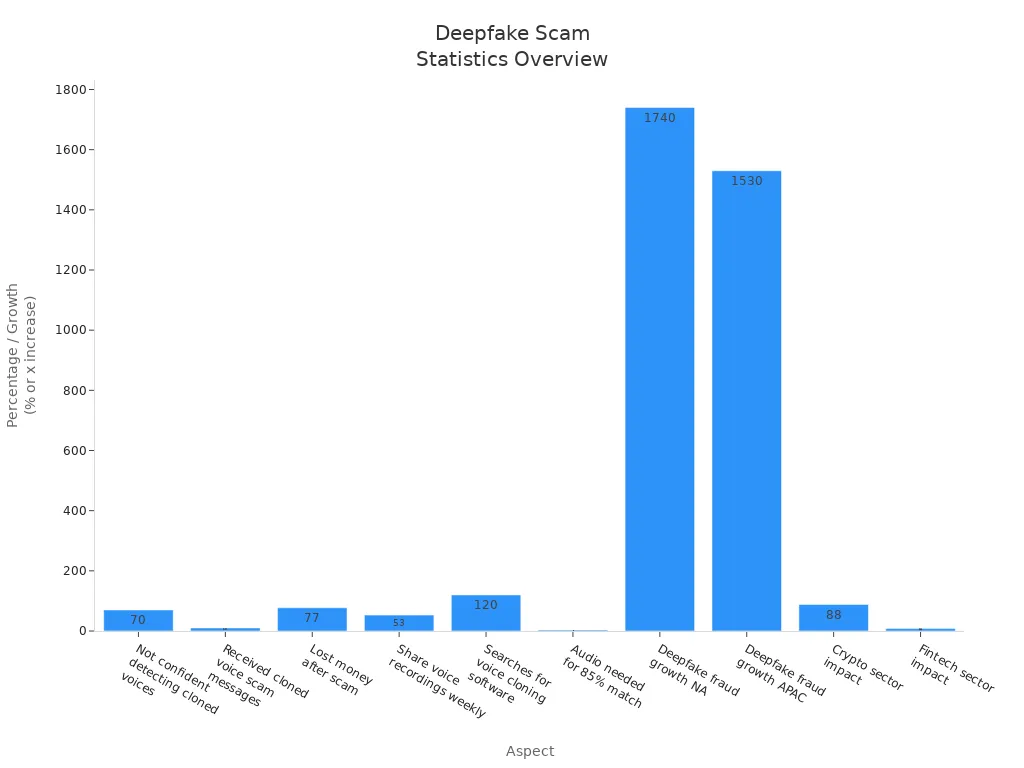
Deepfake fraud cases have gone up by 70% since 2023. Attackers only need a few seconds of audio to copy voices. They use these voices to trick people into sharing private info. These scams often lead to cybercrime, data breaches, and emotional pain.
Zero-Click Malware
Zero-click malware is one of the most dangerous cybercrimes. Attackers find weak spots in smartphone software. They install mobile malware without any user action. Victims do not need to click links or open files. This kind of attack has caused many big data breaches.
|
Year |
Target / Victim |
Attack Name / Operation |
Description / Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|
|
2021 |
Bahraini human rights activist |
ForcedEntry |
Zero-click exploit on iMessage bypassing Apple's BlastDoor security, delivering Pegasus spyware to iPhone 12 Pro. |
|
2019 |
WhatsApp users |
WhatsApp breach |
Zero-day exploit triggered by a missed call, allowing spyware installation without user interaction. |
|
2018 |
Jeff Bezos |
WhatsApp video attack |
Malicious code embedded in a video sent via WhatsApp extracted data from Bezos's iPhone over months without interaction. |
|
2016 |
Activists, diplomats, leaders |
Project Raven (Karma) |
Exploited iMessage flaw using crafted texts to hack iPhones and extract sensitive data without user action. |
Zero-click malware attacks may double in 2025. These attacks show we need better defenses against mobile malware and cybercrime. Users must stay alert to keep their devices safe from hidden threats.
Mobile Security

Mobile security keeps smartphones safe from hackers. It also protects user data. In 2025, new ways make phones harder to attack. People want strong protection that is easy to use. Companies focus on device-based authentication and seamless authentication. They also add advanced security features.
Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication adds more steps to logging in. Users must prove who they are in different ways. A phone might ask for a fingerprint and a code. The code goes to another device. This makes it tough for hackers to get in.
Device-based authentication is important for multi-factor authentication. The phone acts as a trusted device. Many banks and apps use this method now. They send push notifications for approval. This stops most phishing attacks. Biometric authentication adds more safety.
Tip: Always use multi-factor authentication for important accounts. This easy step blocks many attacks.
Seamless authentication lets users log in fast. The process is smooth and does not slow you down. Mobile security uses these tools to keep data safe. It does not make things hard for users.
Passwordless Access
Passwordless authentication changes how people log in. Users do not need passwords. They use device-based authentication and biometric authentication. Phones use fingerprints, facial recognition, or hardware tokens. This removes risks from passwords.
Passwords cause problems. Hackers steal or guess them. About 80% of data breaches use weak or stolen passwords. Passwordless authentication fixes these issues. It uses possession factors like a phone or token. It also uses inherence factors like a fingerprint. Push notifications and adaptive checks add safety.
People like passwordless access because it is easy and safe. About 61% of users prefer it over passwords. If someone loses a device, remote lock and wipe protect the data. Device-based authentication and seamless authentication work together. They stop people who should not get in. Zero Trust policies make sure only the right person gets access.
Mobile security gets better when passwords go away. Users have a better experience and fewer risks.
Secure Boot
Secure boot protects phones when they turn on. The phone checks its software before loading. Only trusted programs can run. This stops hackers from adding bad code at startup.
New advances make secure boot stronger. Phones use hardware-based security modules like Trusted Platform Modules and Secure Enclave. These parts store cryptographic keys and keep data safe. Chipset-level encryption adds more defense. Secure operating systems like GrapheneOS update often. They use sandboxing to block threats.
AI and machine learning help spot threats fast. They find problems as soon as they happen. Secure boot works with device-based authentication. Only trusted users and software can use the phone.
Note: Secure boot is a key part of mobile security. It keeps devices safe from the start.
Seamless authentication and secure boot make a strong shield. Mobile security in 2025 uses these tools. They protect users from new and old threats.
Mobile App Security
Real-Time Threat Detection
Mobile app security uses real-time threat detection to keep users safe. Security teams watch network traffic, logs, and user actions all the time. They use signature checks and behavior analysis to find threats fast. Event correlation helps them see how big a threat is and what it could hurt. When a problem shows up, teams look for the cause and fix it. They might isolate systems or add patches. Adaptive security controls change rules when risks change. Threat intelligence makes finding threats more accurate.
1. Real-time threat detection helps teams stop threats quickly and lowers risk.
2. It lets teams focus on real threats and ignore false alarms.
3. Proactive anomaly detection sets a normal pattern for apps, so problems stand out.
4. Watching all the time helps meet rules for fast breach reporting.
5. Tracking incidents and response times shows if risk goes down and security works well.
AI-powered threat detection and ai-driven malware detection work quietly in the background. They make mobile app security better without slowing users down.
App Permissions
App permissions are important for mobile app security. Apps often want access to contacts, location, camera, or microphone. Users should check these requests and only allow what is needed. Limiting permissions lowers the chance of data leaks and keeps information safe. Many apps now show permission prompts that explain why they need access. This helps users make smart choices. Mobile application security gets better when users stay alert and check permissions often.
Tip: Always check app permissions after you install new apps or updates.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance shapes mobile app security everywhere. Developers must follow strict rules to protect user data and privacy. For example, the European Union needs GDPR compliance, so apps must get clear consent and use privacy-by-design. In the United States, laws like HIPAA, CCPA, and COPPA set rules for health, privacy, and child safety. China wants local data storage, and Brazil uses LGPD for personal data.
|
Region/Market |
Key Regulatory Requirements for Mobile App Security |
|---|---|
|
European Union (EU) |
GDPR, explicit consent, privacy-by-design |
|
United States (USA) |
HIPAA, CCPA, COPPA |
|
China |
Data localization |
|
Brazil |
LGPD |
|
Australia |
Privacy Act, Consumer Law |
|
Industry-Specific |
PCI DSS, NHS guidelines |
|
General |
HTTPS/SSL, 2FA, security testing |
|
App Stores |
Child safety, transparency, payment rules |
|
Accessibility |
European Accessibility Act, WCAG |
Mobile application security depends on following these rules. Apps that follow the rules build trust and avoid fines.
Mobile Application Security
Encryption Protocols
Encryption protocols are very important for mobile app safety. Developers use these tools to keep private data safe from hackers. Most apps use more than one kind of encryption to protect information.
-
AES is the most used symmetric encryption protocol. It comes in three key sizes: 128, 192, and 256 bits. AES-256 gives the best protection for mobile apps.
-
TLS keeps data safe when it moves between apps and servers. It uses both symmetric and asymmetric encryption to keep data private and correct.
-
Asymmetric encryption like RSA and ECC helps with sharing keys and making digital signatures. RSA-2048 and ECC-256 are popular choices for mobile app safety.
-
Diffie-Hellman lets people share keys safely over risky networks.
-
Authentication protocols like certificate-based authentication and OAuth 2.0 check who users are and add more safety.
Developers use AES for stored data, TLS for moving data, and RSA or ECC for managing keys. This mix makes mobile apps much safer. Good key management and regular security checks help stop data loss. End-to-end encryption makes sure only the right person can read the data.
Behavioral Analysis
Behavioral analysis is important for keeping mobile apps safe. AI-powered systems watch for strange actions that could mean fraud or hacking. For example, the system may see a login from a new device or a big money transfer. These things make the app do extra security checks.
Machine learning helps by knowing what normal app actions look like. The system watches how the app works all the time. If it sees odd network requests or changes, it sends alerts. This way, it finds threats that old checks might miss.
Runtime behavior monitoring watches the app while it runs. It looks for odd actions, weak spots, and dangers. This helps keep private data safe and protects the app. Mobile app safety gets better with these smart tools, helping users stay safe from new risks.
User Education
Security Best Practices
Smartphone users need good habits to stay safe. Training works best when it is fun and easy to understand. Short lessons and small group talks help people remember what to do. Role plays and games make learning about security more interesting. Companies should explain security steps in simple words. They should show how these steps protect both work and personal data. People who work from home learn well with videos and regular check-ins.
Learning about security should not happen just once. Talking about it often helps everyone watch out for new dangers. Companies use quizzes and feedback to see if training works. They also check if people follow the rules. Adding digital security to job reviews helps people keep good habits. Step-by-step guides make it easier to learn new security steps and accept changes.
A survey showed most people use lock screens but forget other safety steps. Many do not use VPNs on public WiFi or turn off features they do not need. Knowing about security does not always mean people act safely. Training should teach real actions, like making wireless networks safe and avoiding risky things. Easy-to-use security tools help people build better habits.
Tip: Reminders and simple guides help users make strong security routines.
Phishing Awareness
Phishing attacks go after smartphone users every day. Experts say phishing is the top danger for mobile devices. About 24% of people have faced a mobile phishing attack. Attackers use texts, calls, and emails to trick people into giving away private information. All brands, like Apple, Samsung, and Google, can be at risk.
No phone can stop every phishing attack. The Pixel 9 Pro and Galaxy S24 protect better than some phones, but no phone is perfect. Hollie Hennessy, a security expert, says even the best protections cannot stop all attacks. Users must pay attention and learn how to spot scams.
A simple table shows important facts about phishing:
|
Fact |
Detail |
|---|---|
|
Most common threat |
Phishing |
|
Percentage of users affected |
24% |
|
Devices at risk |
All brands |
|
Best protection |
Pixel 9 Pro, Galaxy S24 |
|
Complete protection |
Not available |
Users should watch for signs of phishing, like strange links or requests for private data. Phishing-resistant authentication blocks many attacks. Staying alert and using good security habits keeps users safe from mobile phishing.
Action Steps
Enable Security Features
Smartphone users should turn on all security features they have. Most phones let you use fingerprint or facial recognition to unlock them. These tools help keep your data safe from people who should not see it. Owners of luxury phones like the Vertu Quantum Flip get even more choices. They can use quantum encryption and AI-powered threat detection. These features give real-time alerts and let you log in with privacy-first options. Businesses can use multi-factor authentication and device-based authentication to keep important information safe. Turning on these features is the first step to strong cybersecurity.
Tip: Always use biometric and device-based authentication for extra safety.
Update Software
Updating your phone’s software keeps it safe. Updates fix problems and close holes that hackers might use. The table below shows how often different brands send updates:
|
Manufacturer/Device Tier |
Update Type |
Frequency |
Duration of Support |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Android (general) |
Major Upgrades |
Once a year |
Varies (2-7 years) |
|
Android (general) |
Security Patches |
Monthly, Bi-monthly, Quarterly, or Bi-annual |
Varies by manufacturer |
|
Samsung Flagship |
Security Patches |
Monthly |
Up to 7 years |
|
Samsung Mid-range/Budget |
Security Patches |
Quarterly |
Up to 7 years |
|
Apple iPhones |
iOS Upgrades & Security Patches |
Monthly or as released |
Typically 6 years |
|
Oppo Find X (High-end) |
Security Patches |
Monthly |
5 years |
|
Oppo Reno/A (Mid-range) |
Security Patches |
Quarterly |
3-4 years |
|
Realme GT |
Security Patches |
Monthly (6 months), then Bi-monthly |
3 years |
|
Xiaomi Devices |
Security Patches |
Quarterly |
Varies by model |
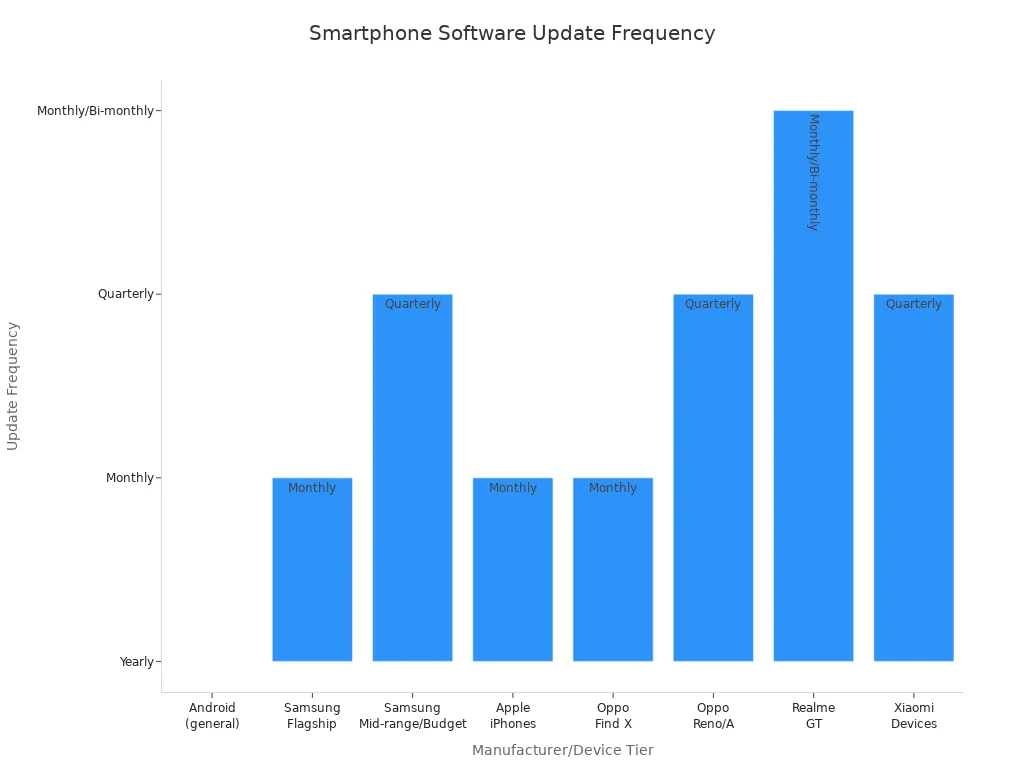
Getting updates every month or every few months keeps your phone safe for a long time. Luxury phones like the Vertu Quantum Flip often give updates for more years, so users stay protected longer.
Monitor Device Activity
Watching what happens on your phone helps find problems early. Users and businesses can use special tools to spot strange actions. Some helpful tools are:
-
FileAudit: Watches who opens or changes files.
-
UserLock: Adds multi-factor authentication and checks who logs in.
-
Automated scripts: Log off users or shut down devices if something odd happens.
These tools look for things like files being opened at weird times or permissions changing when they should not. Finding these problems early can stop data loss. Vertu Quantum Flip owners can use built-in AI to get alerts right away if something looks wrong.
Note: Checking your phone often helps keep your data safe at home and at work.
Future Outlook
Emerging Technologies
Smartphone security will change a lot soon. New biometric technologies will help keep phones safe. DNA analysis, behavioral biometrics, and vein recognition will give users more ways to unlock their phones. These methods are better than just fingerprints or facial recognition. They make it harder for someone else to get into your phone.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning will be more important. These systems can find strange patterns and guess when threats might happen. AI-powered tools will act fast if there is a problem. They can also stop attacks before they start. This makes security smarter and quicker.
Note: New biometric and AI technologies will make smartphones safer and easier to use.
Predictions
Experts think mobile security will have new problems by 2030. Quantum computing will break many old encryption methods. Developers will need to make quantum-resistant algorithms to keep data safe. People will still want both privacy and easy access. Users want things to be simple but also safe.
Human mistakes will still be a weak spot. Social engineering and insider threats will keep causing trouble. Education and technology must work together to lower these risks. Cloud security will be more important as people store more data online. Zero-trust systems and always watching will help protect this data.
A table below shows what experts think will happen by 2030:
|
Prediction Aspect |
Expert Forecast by 2030 |
Explanation and Implications |
|---|---|---|
|
Polymorphic and AI-adaptive malware |
98% of malware will adapt and mutate |
Malware will change to avoid detection. Security must use behavior-based tools and AI-driven defenses. |
|
Predictive Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) |
33% of enterprises will use predictive CTI |
Companies will predict attacks and respond faster by using global threat data and advanced analytics. |
|
Nation-state Actor Dominance |
75% of attacks from nation-state actors |
Attacks will become stealthier and more political. Organizations must use advanced detection and threat sharing. |
Tip: Using many layers of defense, learning, and teamwork will help keep people safe in the future.
Luxury phones like the Vertu Quantum Flip help keep data safe. People use mobile payments and biometric authentication every day. Good habits like updating software and using strong passwords lower risks. Learning about new threats helps people stay safe.
Knowing what is happening and using smart habits keeps users safe from new dangers. As phones get better, making smart choices and learning often is important for safety.
FAQ
What makes the Vertu Quantum Flip different from regular smartphones?
The Vertu Quantum Flip has quantum encryption and AI-powered security. It is made with fancy materials and gives special perks. Owners get alerts about threats right away. They can log in with privacy-first options. This phone is safer and more stylish than most others.
How does quantum encryption protect my data?
Quantum encryption uses hard math to lock messages and files. Hackers cannot break it with normal computers. This keeps your personal information safe from cybercriminals.
Why should users enable biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication uses your fingerprint or face to unlock the phone. This makes it tough for others to get in. It gives your personal data extra protection.
How often should users update their smartphone software?
Experts say you should check for updates every month. Updates fix security problems and add new things. Doing this often helps keep your device safe from new threats.
Can AI-powered security stop all cyberattacks?
AI-powered security finds and blocks many threats fast. But no system can stop every attack. Users should stay careful and use good safety habits for the best protection.