The Breakthrough: 100 Sub-Agents, 1,500 Tool Calls, 4.5x Speed Increase—Native Multimodal AI Redefining Agentic Intelligence
Kimi K2.5 represents the most powerful open-source model to date, achieving state-of-the-art coding and vision capabilities through native multimodal architecture trained on approximately 15 trillion mixed visual and text tokens. The Agent Swarm Innovation: Self-directed orchestration of up to 100 sub-agents executing parallel workflows across up to 1,500 tool calls, reducing execution time by 4.5x compared to single-agent setups—automatically created and coordinated without predefined workflows. The Coding Revolution: Strongest open-source coding model with exceptional front-end capabilities, turning simple conversations into complete interactive layouts with rich scroll-triggered animations, excelling at visual debugging by reasoning over images/video to improve image-to-code generation and lower barriers for visual intent expression. The Cost Advantage: Delivering strong performance on agentic benchmarks (HLE, BrowseComp, SWE-Verified) at fraction of competitor costs. The Office Productivity: Handling high-density large-scale work end-to-end, reasoning over massive inputs, coordinating multi-step tool use, delivering expert-level documents/spreadsheets/PDFs/slides through conversation—59.3% improvement on AI Office Benchmark and 24.3% improvement on General Agent Benchmark over K2 Thinking. The PARL Training: Parallel-Agent Reinforcement Learning with trainable orchestrator decomposing tasks into parallelizable subtasks, frozen subagents executing concurrently, staged reward shaping preventing serial collapse, critical-steps metric forcing parallel strategies. Availability: Via Kimi.com, Kimi App, API (platform.moonshot.ai), and Kimi Code—four modes (K2.5 Instant, Thinking, Agent, Agent Swarm Beta).
Part I: The Multimodal Foundation
Massive-Scale Vision-Text Joint Pretraining
Training Corpus: Approximately 15 trillion mixed visual and text tokens
Architecture: Native multimodal model from ground up
Key Insight: “At scale, the trade-off between vision and text capabilities disappears—they improve in unison”
Result: State-of-the-art performance in both coding and vision tasks
Paradigm Shift: Vision and text not competing but complementary
The Unified Capability Emergence
Traditional Approach: Separate text and vision models
Kimi K2.5 Innovation: Single model excelling at both
Synergistic Learning: Visual reasoning enhancing code understanding
Practical Impact: Seamless multimodal workflows
Part II: Coding with Vision—The Front-End Revolution
Conversational Interface Generation
Capability: Turning simple conversations into complete front-end interfaces
Features Implemented:
- Interactive layouts
- Rich animations
- Scroll-triggered effects
- Complex UI components
Single Prompt Power: Complete implementations from minimal descriptions
Example: Image-gen tool integration producing fully functional interfaces
Developer Impact: Dramatically reduced front-end development time
Visual Debugging Breakthrough
The Innovation: Reasoning over images and video for code generation
Image-to-Code: Converting visual designs directly to implementation
Video-to-Code: Reconstructing websites from video demonstrations
Example Workflow:
- Record video of desired website behavior
- Feed to K2.5
- Receive complete code reconstruction
- Iterate based on visual feedback
Barrier Reduction: Users expressing intent visually instead of technical specifications
Autonomous Visual Iteration
Kimi Code Integration: Terminal-based tool integrating with VSCode, Cursor, Zed
Open Source: Freely available codebase
Multimodal Input: Supports images and videos
Auto-Discovery: Automatically finds and migrates existing skills and MCPs
Example – Matisse's La Danse Translation:
- Visual input: Famous painting aesthetic
- Documentation lookup: Kimi App design guidelines
- Visual inspection: K2.5 checking own output
- Autonomous iteration: Refining until aesthetically matching
- End-to-end result: Art-inspired webpage created autonomously
The Breakthrough: AI visually debugging its own work without human intervention
Real-World Software Engineering
Kimi Code Bench: Internal benchmark covering diverse end-to-end tasks
Task Categories:
- Building from scratch
- Debugging existing code
- Refactoring for improvements
- Testing implementation
- Scripting automation
Language Coverage: Multiple programming languages
K2.5 vs K2 Improvement: Consistent and meaningful gains across all task types
Production Readiness: Strong performance on real-world engineering workflows
Visual Reasoning Example
Puzzle Solving: K2.5 analyzing visual puzzle
Code-Based Marking: Using code to mark shortest path solution
Integration: Vision understanding + code generation + logical reasoning
Practical Applications:
- Algorithm visualization
- Game development
- Educational tools
- Interactive problem solving
Part III: Agent Swarm—Scaling Out, Not Just Up
The Paradigm Shift
Traditional Scaling: Single agent with more compute (scaling up)
K2.5 Innovation: Multiple coordinated agents (scaling out)
Research Preview: Agent Swarm currently in beta
Shift Significance: From sequential to parallel agentic execution
The Technical Architecture
Orchestrator Agent: Trainable coordinator (not frozen)
Sub-Agents: Up to 100 dynamically instantiated (frozen during execution)
Task Decomposition: Breaking complex tasks into parallelizable subtasks
Dynamic Instantiation: Sub-agents created on-demand for specific roles
Example Roles:
- AI Researcher
- Physics Researcher
- Fact Checker
- Data Analyst
- Code Reviewer
No Predefined Workflows: Entirely self-directed coordination
Parallel-Agent Reinforcement Learning (PARL)
The Challenge: Training reliable parallel orchestrator
Problem 1 – Delayed Feedback: Sparse rewards from independently running sub-agents
Problem 2 – Non-Stationary: Sub-agent behaviors changing during training
Problem 3 – Serial Collapse: Orchestrator defaulting to single-agent despite parallel capacity
The Solution – Staged Reward Shaping:
Reward Function:
R_t = λ_aux(e) · r_parallel + (1 - λ_aux(e)) · (I[success] · Q(τ))
↑ ↑
instantiation reward task-level outcome
Annealing Schedule: λ_aux decreases from 0.1 → 0.0 over training
Early Training: Auxiliary reward r_parallel incentivizes sub-agent instantiation
Late Training: Focus shifts to end-to-end task quality Q(τ)
Prevents: Degenerate solutions where parallelism exists nominally but not effectively
The Critical Steps Metric
Traditional Metric: Total steps counted
Problem: Doesn't capture parallel execution benefits
Critical Steps Definition:
CriticalSteps = Σ(S_main(t) + max_i S_sub,i(t))
Components:
- S_main(t): Orchestration overhead at time t
- max_i S_sub,i(t): Slowest sub-agent at time t
Inspiration: Critical path in parallel computation theory
Forcing Function: Spawning more subtasks only helps if shortening critical path
Result: Genuine parallel strategies emerge during training
Performance Improvements
End-to-End Runtime Reduction: Up to 80%
Speedup Factor: 3x–4.5x compared to single-agent execution
Critical Steps Reduction: 3x–4.5x fewer steps to achieve target performance
Scaling Behavior: Savings increase as task complexity rises
Wall-Clock Impact: 4.5x time reduction via parallelization
Complex Workloads: Enables longer-horizon tasks previously impractical
Execution Capacity
Maximum Sub-Agents: 100 concurrent
Maximum Tool Calls: 1,500 coordinated steps
Coordination Complexity: Automatic orchestration without manual workflow design
Benchmark Performance: Strong results on HLE, BrowseComp, SWE-Verified
Cost Efficiency: Fraction of competitor costs while maintaining performance
Training Progress Visualization
Smooth Reward Increase: Gradual improvement throughout training
Parallelism Level: Gradually increasing agent coordination
Convergence: Stable final performance without collapse
Reliability: Production-ready coordination mechanisms
Part IV: Office Productivity Revolution
Real-World Knowledge Work
Target: High-density, large-scale office tasks
End-to-End Handling: From input to finished deliverable
Output Formats:
- Microsoft Word documents
- Excel spreadsheets
- PDF files
- PowerPoint slide decks
Interface: All through natural conversation
Advanced Office Capabilities
Word Processing:
- Adding annotations
- Complex formatting
- Long-form content (10,000+ words)
Spreadsheet Mastery:
- Financial model construction
- Pivot Table creation
- Advanced formulas
PDF Generation:
- LaTeX equation writing
- Professional formatting
- 100+ page documents
Presentation Creation:
- Slide deck generation
- Visual design
- Content organization
Internal Expert Productivity Benchmarks
AI Office Benchmark: Evaluates end-to-end Office output quality
General Agent Benchmark: Measures multi-step production workflows against human experts
K2.5 vs K2 Thinking Improvements:
- 59.3% improvement on AI Office Benchmark
- 24.3% improvement on General Agent Benchmark
Real-World Focus: Tasks professionals actually perform daily
Expert-Level Output: Matching or exceeding human professional quality
Time Compression
Previous Reality: Tasks taking hours or days
K2.5 Performance: Minutes to completion
Productivity Multiplier: 10x-100x time savings potential
Workflow Integration: Seamlessly fitting into existing processes
Professional Impact: Redefining knowledge worker productivity
Part V: Benchmark Performance Deep Dive
Coding Benchmarks
SWE-Bench Series (Verified, Multilingual, Pro):
- Minimal toolset (bash, createfile, insert, view, strreplace, submit)
- Tailored system prompts
- Non-thinking mode optimal
- Averaged over 5 independent runs
Terminal-Bench 2.0:
- Default Terminus-2 agent framework
- JSON parser provided
- Non-thinking mode for compatibility
CyberGym: Claude Opus 4.5 comparison under non-thinking setting
Kimi Code Bench: Strong improvements across all task categories
Vision Benchmarks
MMMU-Pro: Official protocol, input order preserved, images prepended
WorldVQA: Atomic vision-centric world knowledge evaluation (github.com/MoonshotAI/WorldVQA)
OmniDocBench: Score = (1 – normalized Levenshtein distance) × 100
ZeroBench (with tools): Multi-step reasoning with 24k tokens per step, 30 max steps
Averaging: 3 runs (avg@3) for consistency
Agentic Search Benchmarks
Tools Equipped: Search, code-interpreter, web-browsing
Context Management: No management except BrowseComp (discard-all strategy)
Context Overflow: Tasks exceeding limit counted as failed
System Prompts: Emphasizing deep and proactive tool use
Averaging: 4 runs (avg@4) for Seal-0 and WideSearch
Reasoning Benchmarks
HLE (Text & Image):
- Full set: Text 31.5, Image 21.3 (without tools)
- Full set: Text 51.8, Image 39.8 (with tools)
- 96k token completion budget
- Hugging Face access blocked (prevent data leakage)
AIME 2025: 96k token budget, avg@32 (32 runs)
HMMT 2025 (Feb): 96k token budget, avg@32
GPQA-Diamond: 96k token budget, avg@8
IMO-AnswerBench: 96k token budget
Long-Context Performance
AA-LCR: Averaged over 3 runs (avg@3)
LongBench-V2: Identical prompts, input standardized to ~128k tokens
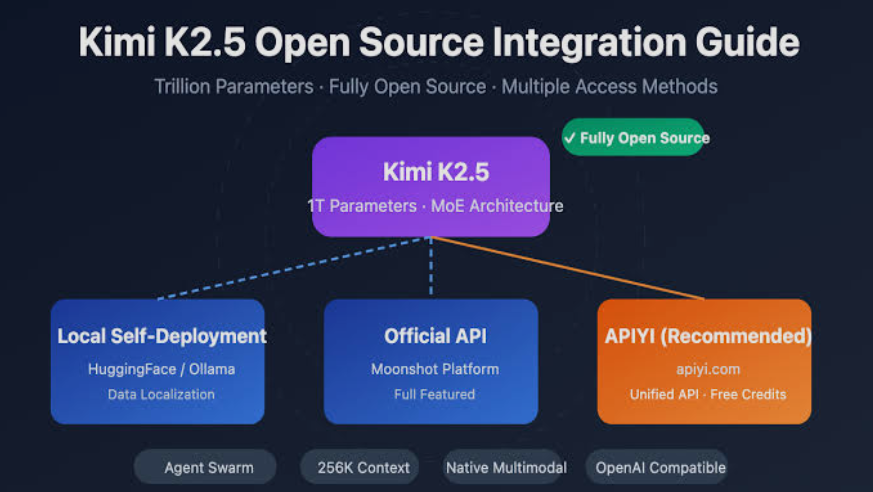
Context Length: 256k tokens supported
Part VI: Access and Availability
Four Modes Available
K2.5 Instant: Fast responses for simple queries
K2.5 Thinking: Extended reasoning for complex problems
K2.5 Agent: Tool-augmented execution with preconfigured capabilities
K2.5 Agent Swarm (Beta): Multi-agent parallel coordination
Beta Access: Agent Swarm with free credits for high-tier paid users
Platform Options
Kimi.com: Web-based interface with all four modes
Kimi App: Mobile/desktop application
API: platform.moonshot.ai for developer integration
Kimi Code: Terminal-based coding assistant
Open Source: Kimi Code released as open-source project
Configuration Details
Temperature: 1.0 (default)
Top-p: 0.95 (default)
Context Length: 256k tokens
Reproducibility: Official API recommended for benchmark recreation
Vendor Verification: Kimi Vendor Verifier (KVV) for third-party services
Part VII: The Road to AGI
Meaningful Step Forward
For Open-Source Community: Most powerful model demonstrating real-world capability
Under Real Constraints: Strong performance within practical limitations
Production Readiness: Suitable for actual knowledge work deployment
The Future Direction
Continued Advancement: Pushing further into agentic intelligence frontier
Boundary Redefinition: Challenging assumptions about AI capabilities in knowledge work
Research Focus: Expanding parallel coordination and visual reasoning
Open Ecosystem: Contributing to accessible AI advancement
Conclusion: Visual Agentic Intelligence Arrives
The Three Pillars
1. Coding with Vision: Native multimodal architecture enabling visual debugging and image-to-code workflows
2. Agent Swarm: Self-directed parallel coordination with up to 100 sub-agents and 1,500 tool calls
3. Office Productivity: Expert-level document/spreadsheet/PDF/slide generation through conversation
The Performance Story
59.3% improvement on AI Office Benchmark over K2 Thinking
24.3% improvement on General Agent Benchmark
4.5x speedup through agent swarm parallelization
State-of-the-art coding and vision capabilities
Fraction of cost compared to proprietary competitors
The Technical Innovation
15 trillion tokens of vision-text joint pretraining
PARL training with staged reward shaping
Critical-steps metric forcing genuine parallelism
No predefined workflows in agent orchestration
Autonomous visual debugging capability
The Accessibility
Open-source model pushing frontier forward
Multiple access points: Web, app, API, terminal
Four operational modes for different use cases
Beta features with free credits for experimentation
The Paradigm Shift
From sequential to parallel agent execution
From text-only to native multimodal reasoning
From hours to minutes for complex knowledge work
From predefined to self-directed workflow coordination
Get Started:
- Web: https://www.kimi.com
- API: https://platform.moonshot.ai
- Code: https://www.kimi.com/code
- Modes: Instant, Thinking, Agent, Agent Swarm (Beta)
Technical Report: Full details including prompts and methodology forthcoming
Vendor Verification: https://kimi.com/blog/kimi-vendor-verifier.html
WorldVQA Benchmark: https://github.com/MoonshotAI/WorldVQA
The Bottom Line: Kimi K2.5 represents the most powerful open-source model to date, achieving breakthrough performance through native multimodal architecture (15T vision-text tokens), self-directed agent swarm coordination (100 sub-agents, 1,500 tool calls, 4.5x speedup), state-of-the-art coding with vision (autonomous visual debugging), and expert-level office productivity (59.3% AI Office improvement, 24.3% General Agent improvement). The combination of visual agentic intelligence with PARL-trained parallel orchestration marks meaningful step toward AGI for open-source community, demonstrating strong capability on real-world tasks under real-world constraints at fraction of proprietary model costs. Access via Kimi.com, app, API, and open-source Kimi Code terminal tool across four modes (Instant/Thinking/Agent/Agent Swarm Beta). The future of agentic intelligence is parallel, visual, and open.
Try Agent Swarm Beta: Experience 100-agent coordination redefining knowledge work efficiency. 🦞✨