You usually take between 12 and 20 breaths per minute when you rest. This normal breathing rate keeps your body balanced and healthy. Breathing rate means how many times you breathe in and out in one minute. The table below shows how the typical breathing rate stays within this range for most adults:
|
Age Group (years) |
Median Breathing Rate (brpm) |
|---|---|
|
39–48 |
15.6 |
|
79–88 |
17.0 |
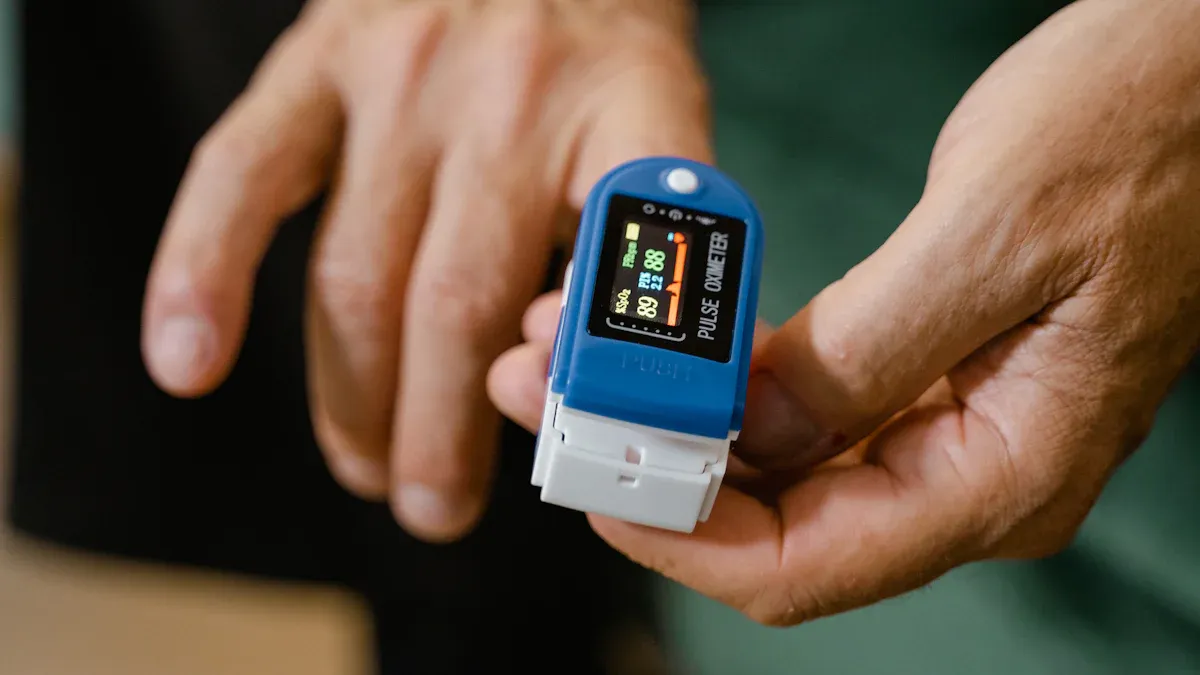
Breathing is one of your main vital signs. Tracking your normal breathing rate helps you spot changes early. Most people have small ups and downs in their breathing. If you notice big changes, it may signal a health problem. You can use smart tools like the Aura ring to watch your breathing and keep your vital signs in check.
Key Takeaways
-
Most healthy adults breathe 12 to 20 times each minute when resting. This helps keep the body balanced and healthy.
-
Breathing rate can change with age, activity, feelings, and health problems. Tracking your breathing rate helps find early signs of trouble.
-
You can check your breathing rate at home. Count your breaths for one full minute while you sit quietly and feel calm.
-
Breathing faster than 20 or slower than 12 times per minute may mean health problems. You should see a doctor if this happens.
-
Smart devices like the Aura Ring make it easy to watch your breathing all the time. You can also share this information with your doctor.
Normal Breathing Rate
Normal Range of Respiratory Rate
To find your breathing rate, count your breaths for one minute. Most healthy adults breathe 12 to 20 times each minute when resting. This range helps your body keep oxygen and carbon dioxide balanced. Doctors and nurses use this number to check your respiratory health.
Recent guidelines say adults at rest should breathe within this range. This balance gives your body the oxygen it needs and removes carbon dioxide. The normal respiratory rate can change a bit with age or health. Still, it is always an important part of your vital signs.
Large studies show most adults breathe about 18 to 20 times per minute. The table below shows breathing rates for different adult groups:
|
Age Group |
Normal Respiratory Rate (breaths per minute) |
|---|---|
|
Adults (general) |
15–18 |
|
Adults (~50 years) |
18–25 |
|
Elderly (≥ 65 years) |
12–28 |
|
Very Elderly (≥ 80 years) |
10–30 |
Another study checked thousands of hospital patients. Most adults had a breathing rate between 18 and 20 breaths per minute. The chart below shows average breathing rates for different groups:
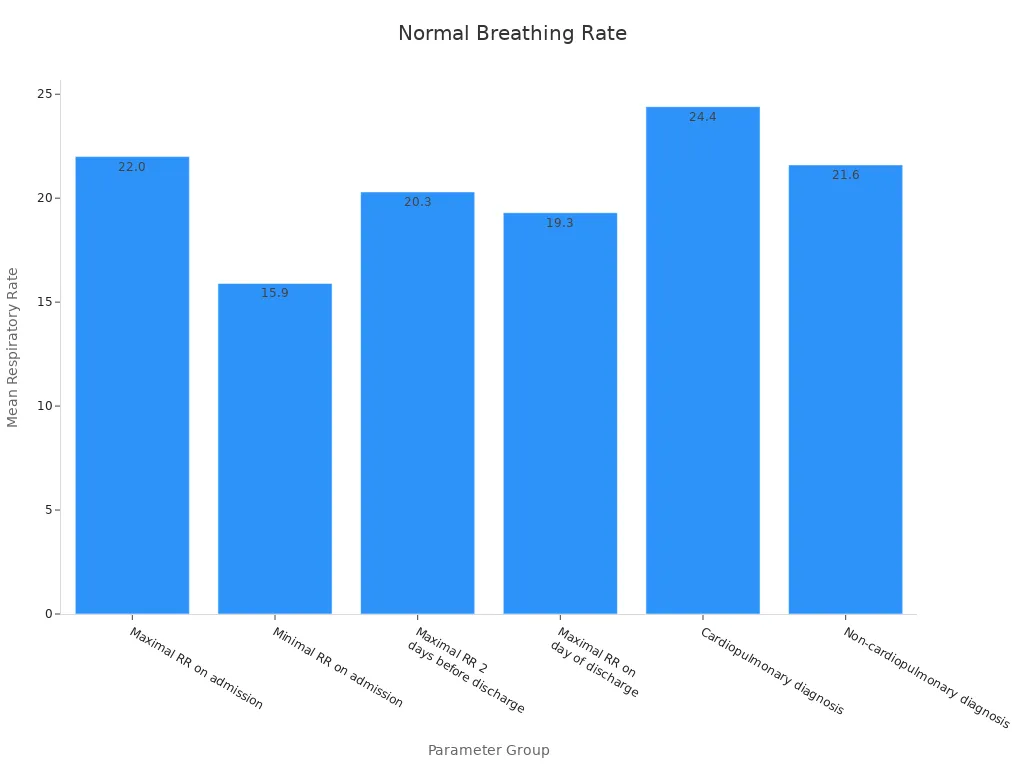
You can see the normal range stays steady, even for people with heart or lung problems. This makes it a good sign of your health.
Tip: When you check your breathing rate, count for at least two minutes. This gives you a better number and helps you notice changes in your normal breathing rate.
Factors Affecting Breathing Rate
Many things can change your breathing rate. Physical activity is a big reason. When you exercise, your body needs more oxygen, so you breathe faster. After you stop, your breathing rate goes back to normal.
Emotions can also change how you breathe. If you feel scared or nervous, you may breathe faster. Fever can make your breathing rate go up as your body cools down.
Health problems can affect your normal respiratory rate. Asthma, pneumonia, and heart problems often make you breathe faster. Dehydration and allergies can also change your breathing.
Your lifestyle and where you live matter, too. Smoking, drinking alcohol, and being around dust or fumes can raise your breathing rate. Bad air quality inside or outside can cause breathing problems. Clean air and good ventilation help your lungs and keep your breathing steady.
Other things like age, gender, and the season can change your breathing rate. Older adults may have a wider range of normal respiratory rates.
Note: Your breathing is one of your vital signs. Changes in your breathing rate show how your body reacts to stress, sickness, or the environment. Watching your normal breathing rate helps you know about your health.
Normal Respiratory Rate for Adults
Age Differences
You may notice that your breathing changes as you get older. The normal respiratory rate for adults can shift with age. A large study of 10,000 healthy adults found that most people breathe between about 12 and 20 times per minute at rest. The average rate is around 15.4 breaths per minute. This study also showed that your breathing rate can decrease slightly as you age. Women under 50 often have a higher rate than men, and your body mass index (BMI) can also play a role.
The table below shows how the normal respiratory rate changes in different age groups:
|
Age Group (years) |
Respiration Rate (breaths/min) Mean (SD) |
Abdominal Movement (AM) Mean (N) |
Thoracic Movement (TM) Mean (N) |
AM/(AM+TM) (%) |
Vital Capacity (ml) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
20–29 |
14.7 (4.04) |
1.57 (1.70) |
2.85 (1.55) |
28.3 (23.1) |
4169 (848) |
|
30–39 |
16.9 (5.32) |
1.28 (1.21) |
3.21 (1.70) |
31.1 (26.1) |
3833 (1207) |
|
40–49 |
15.7 (5.25) |
2.02 (1.80) |
3.34 (2.41) |
37.1 (21.8) |
3335 (944) |
|
50–59 |
18.1 (5.54) |
2.37 (1.83) |
3.46 (2.31) |
42.3 (20.7) |
3120 (677) |
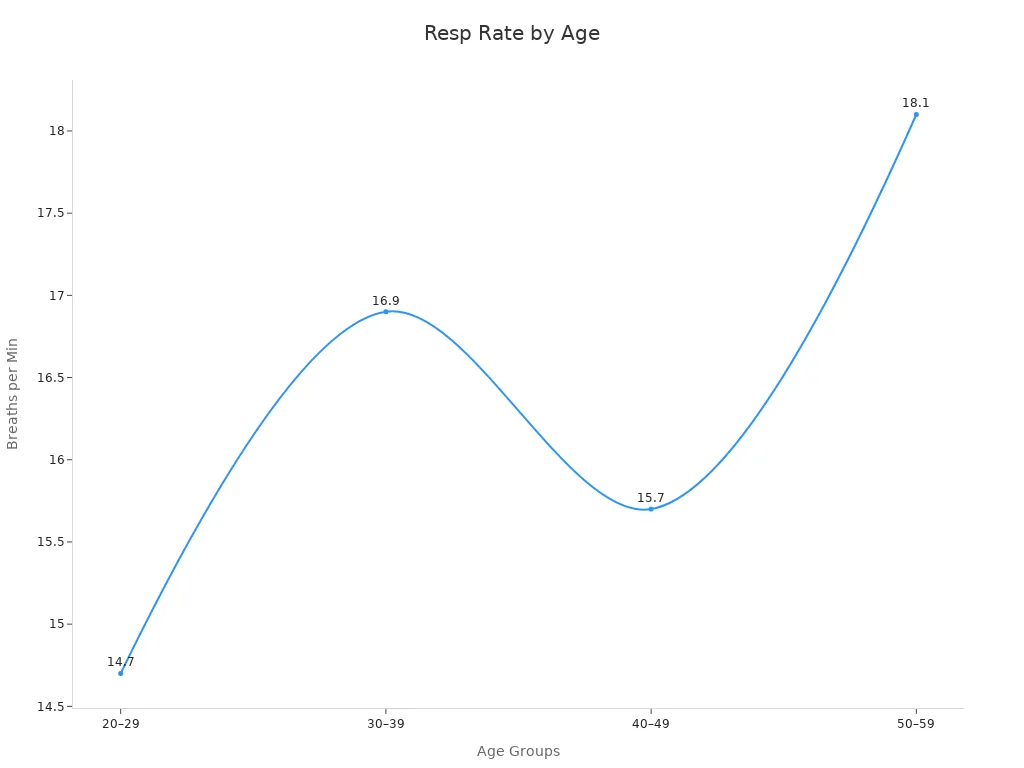
As you age, your breathing may become a bit faster, and you may use your abdominal muscles more. Your lung capacity also tends to decrease. These changes are normal and happen to most adults.
Note: Even with these differences, the normal respiratory rate for adults stays within a steady range for most people.
When Is It Abnormal?
You should pay attention if your breathing rate falls outside the normal range. For adults, a normal respiratory rate is 12 to 20 breaths per minute at rest. If you notice your breathing rate goes above 20, doctors call this tachypnea. This can signal problems like pneumonia, asthma, heart failure, or infection. If your rate drops below 12, this is called bradypnea. It may be linked to brain injuries, certain diseases, or exposure to toxins.
Here are some signs that your breathing rate may be abnormal:
-
Breathing faster than 20 times per minute (tachypnea)
-
Breathing slower than 12 times per minute (bradypnea)
-
Feeling short of breath or having trouble breathing (dyspnea)
-
Blue or gray color in your lips, nails, or skin (cyanosis)
-
Chest pain or tightness
-
Pulling in of the chest wall with each breath (intercostal retractions)
-
Fever with a rapid breathing rate
If you notice a rapid change in your breathing rate, especially with these symptoms, you should seek medical help right away.
Doctors use careful methods to measure your breathing rate. They often count for a full minute and try to make sure you do not know they are watching. This helps them get the most accurate number. The normal respiratory rate for adults is a key sign of your health, so tracking it can help you catch problems early.
Measuring Breathing Rate
At-Home Methods
You can measure your breathing rate at home with a few simple steps. This helps you keep track of your health and spot changes early. Here is a step-by-step guide to counting your breaths per minute:
-
Rest for a few minutes before you start.
-
Sit upright in a chair or on your bed and relax.
-
Watch your chest or abdomen rise and fall.
-
Count each rise as one breath.
-
Keep counting for one full minute.
-
Write down the number of breaths you counted.
-
If you find it hard to count your own breathing, ask someone to help.
-
Try not to think about your breathing while counting, as this can change your natural rate.
Tip: For the most accurate result, avoid eating, drinking, or exercising for at least 30 minutes before measuring your breathing rate.
Manual counting remains a reliable way to check your breathing at home. Studies show that following these steps gives you a good estimate of your breathing rate. At-home monitoring is important for people with chronic breathing problems and helps you notice changes in your vital signs.
Using Smart Devices
Smart devices make it even easier to track your breathing rate. The VERTU Aura Ring uses advanced AI health monitoring to measure your breathing without any effort from you. You simply wear the ring, and it quietly tracks your breathing, heart rate, blood oxygen, and other health metrics all day and night.
The Aura Ring fits comfortably on your finger, so you can wear it all the time. Its nano-sensor chip checks your breathing rate and other vital signs with high accuracy. You get weekly wellness reports that show your breathing patterns and other health trends. This helps you spot changes early and take action if needed.
Clinical studies have shown that wearable devices can measure breathing rates as accurately as hospital equipment. These devices work well for healthy adults and people with health problems. With the Aura Ring, you get continuous monitoring, easy-to-read reports, and support from health experts. This makes it simple to keep your breathing and overall health on track.
Abnormal Breathing Rate Causes

High Breathing Rate
Your breathing can get faster when you exercise or feel stressed. But if you breathe fast while resting, it could mean something is wrong. Adults who breathe more than 20 times each minute have a high breathing rate. This can happen if you have a fever, are dehydrated, or feel pain. Heart failure, lung disease, or problems with your body’s chemicals can also cause fast breathing. Panic attacks or strong feelings can make you breathe quickly too.
A big study showed that 13.8% of adults breathed 18.6 times or more each minute. High breathing rates are often seen in older people, people with obesity, diabetes, or those who smoke. The table below shows what the study found:
|
Factor |
Association with High Breathing Rate |
|---|---|
|
Age |
Higher rates in older adults |
|
Abdominal obesity |
Increased risk |
|
Diabetes |
Stronger effect in men |
|
Smoking |
Higher rates |
|
Low education |
More common in women |
Breathing fast can be an early sign that your health is getting worse, especially if you have other symptoms.
Low Breathing Rate
If you breathe less than 12 times each minute, your breathing rate is low. This can happen if you take some medicines or have a brain injury. Some people with heart or lung problems may also breathe slowly. Breathing slowly, between 4 and 10 times each minute, can sometimes help your heart and breathing muscles. But if you feel sleepy, confused, or have trouble breathing, slow breathing can be dangerous.
Doctors have found that slow breathing can help treat some diseases like asthma. It can also help your heart and lungs work better together. Still, you should watch for changes, especially if you do not feel well.
Warning Signs
You should look out for warning signs that come with abnormal breathing. These signs mean you may need help from a doctor right away:
-
Trouble breathing or shortness of breath
-
Fast, shallow breaths
-
Blue lips or skin
-
Chest pain, especially when you breathe in
-
Feeling very tired or confused
-
Fast heartbeat
-
Coughing up mucus
-
Fever
Even small chest pain or trouble breathing can raise your risk for heart problems or stroke. If you notice these symptoms, do not wait. They could mean you have a serious problem that needs quick care.
When to Seek Medical Help
Red Flags
You should know when your breathing changes mean you need to see a doctor. Some signs show that your body may have a serious problem. Watch for these red flags:
-
Coughing up blood
-
A cough that lasts more than three weeks
-
Feeling tired all the time or losing weight without trying
-
Trouble breathing that gets worse or does not go away
If you notice more than one of these signs together, the risk of a serious illness goes up. Doctors use these warning signs to decide if you need urgent care. People with high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart problems should pay extra attention to changes in breathing. If you wake up gasping, snore loudly, or feel sleepy during the day, you may have a sleep problem that needs testing. Early checks help adults get the right treatment fast.
Tip: Always tell your doctor if you have new or lasting breathing problems, especially if you have other health issues.
Monitoring Over Time
Keeping track of your breathing over days or weeks helps you spot changes early. Wearable devices now let you check your breathing rate all day and night. These tools can show patterns that you might miss. Studies show that continuous monitoring helps doctors find problems sooner in people with breathing or heart conditions.
-
Wearable sensors track your breathing without wires or discomfort.
-
Some devices, like smart rings, give you weekly reports and health tips.
-
Continuous monitoring can help lower the risk of sudden breathing problems.
-
Doctors use this information to adjust your care and keep you safe.
The COVID-19 pandemic showed how important it is to watch breathing closely, especially for adults with lung or heart disease. While more research is needed, many people find that wearable devices make it easier to manage their health. You can use these tools to share your breathing data with your doctor and get help before problems get worse.
Most adults breathe 12 to 20 times each minute. Checking your breathing often helps you notice changes early. This keeps you healthy. Nurses check your breathing more than once to be sure the number is right. Devices like the VERTU Aura Ring help you watch your vital signs every day. If you see strange symptoms, tell your doctor. Paying attention and using smart tools can help you feel sure about your health.
FAQ
What is the best time to measure my breathing rate?
You get the most accurate result when you measure your breathing rate while resting. Sit quietly for a few minutes before you start. Avoid checking right after exercise, eating, or feeling stressed.
Can the VERTU Aura Ring track my breathing rate while I sleep?
Yes, the Aura Ring tracks your breathing rate all night. You can see your sleep breathing patterns in your weekly wellness report. This helps you spot changes that may affect your health.
What should I do if my breathing rate is always high or low?
If you notice your breathing rate stays above 20 or below 12 breaths per minute, talk to your doctor. Watch for other symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. Early action helps you stay healthy.
How does the Aura Ring compare to manual counting?
The Aura Ring uses advanced sensors to track your breathing rate automatically. You do not need to count or write anything down. You get continuous, accurate data and helpful reports right on your phone.




